Quantified Buildings and Modelling
Abstract
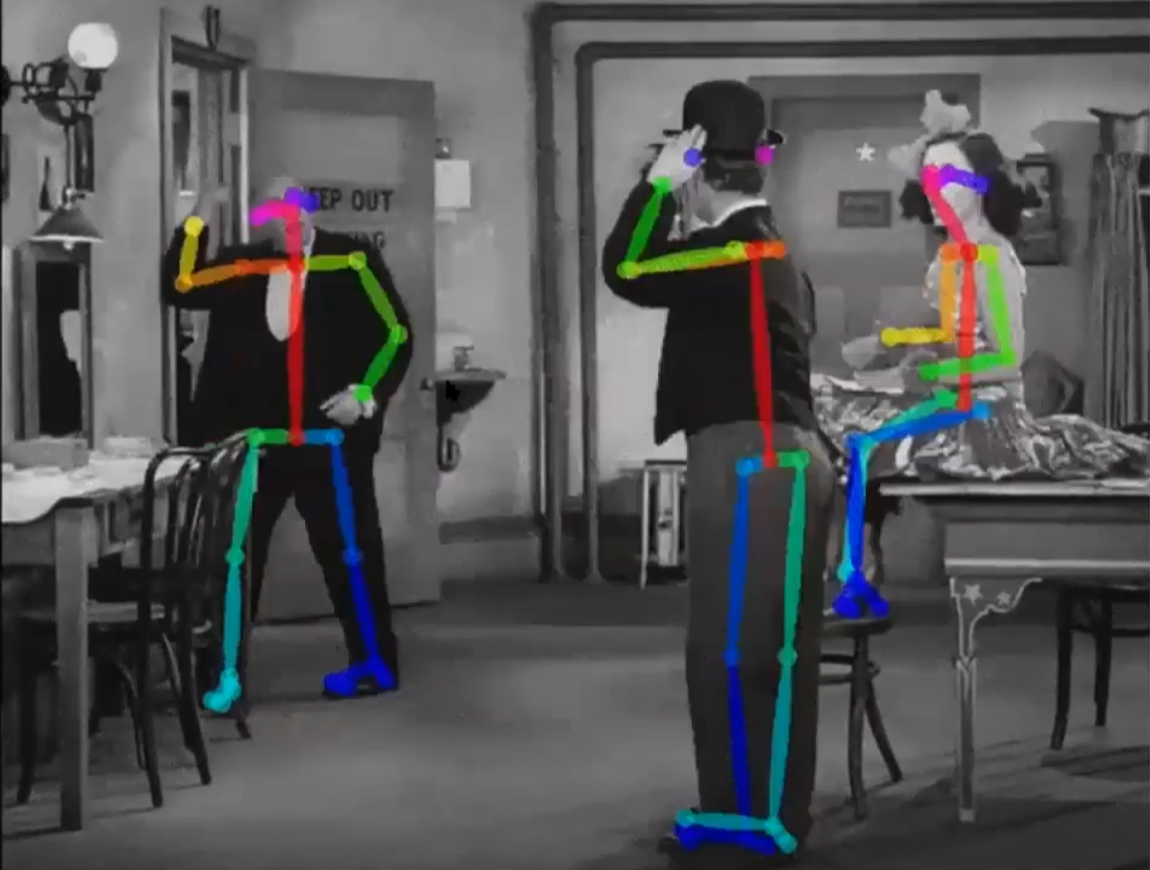
In Professor David Kirsch's illuminating keynote, he articulates the emergent concept of "quantified buildings," underscoring an intricate exploration of human behavioural dynamics within architectural confines. Despite the significant amount of time spent indoors—surpassing 85% of human life—Kirsch posits a glaring void in empirical insights and scientific exploration concerning interactions within the built environment.
Kirsch’s discourse gravitates towards an innovative fusion of sensor technology and machine learning, envisaging a paradigm where vast datasets become instrumental in extrapolating nuanced human behaviours, anchored in contextualized architectural and environmental settings. The professor extrapolates on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) agents within three-dimensional simulated environments, postulating a novel methodology for assessing and refining architectural designs. This is predicated on predictive analytics, providing insights into occupant behaviours and social dynamics, contingent on diverse architectural nuances.
The keynote delineates intrinsic challenges manifest in this innovative trajectory. Human behaviours, characterized by their complexity and the multifaceted interplay within shared architectural spaces, present nuanced variables that defy simplistic analytical frameworks. However, Kirsch’s conclusive stance resonates with optimism, suggesting that surmounting these intricate challenges can precipitate a renaissance in both architectural design and cognitive science. Such advancements would inaugurate edifices and spaces intrinsically attuned to human behavioural patterns, predilections, and interactive dynamics, marking a seminal departure from extant paradigms.
Presentation
Conference Paper
Keywords
Quantified Buildings, Human Behavioural Dynamics, Sensor Technology, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence Agents, Three-Dimensional Simulated Environments, Predictive Analytics, Social Dynamics, Cognitive Science, Architectural Design
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.47330/DCIO.2021.BXMI1626
Bibliography
PENDING