Enhancing a Built Asset’s Operations for Seismic Excitations: An Integration of Machine Learning & BIM
Abstract
The increased levels of urbanisation in coordination with the rapid growth of the human population require modern cities to align with uncertain phenomena that take place within their built environment and grant particular attention in securing the safety and providing a high quality of livelihood to their citizens. Natural disasters and in particular the increased occurrence frequency of phenomena such as seismic excitations, threaten modern cities aim, because their impact results to destructive consequences within the built environment that they take place.
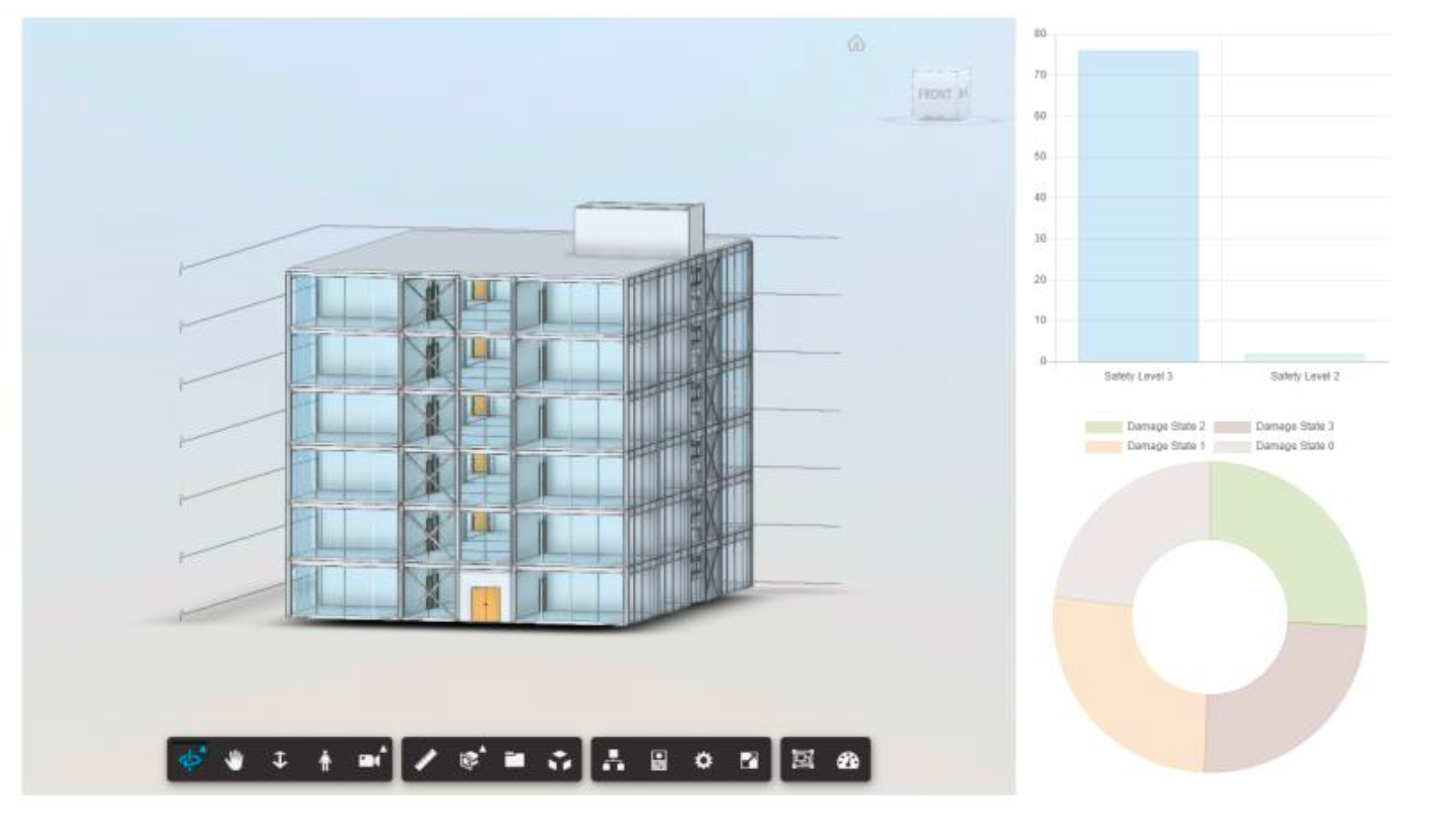
During the phases of disaster management lifecycle of seismic excitations, the discipline of achieving efficient building operation has arisen that requires effective communication, share of information and efficient evaluation of the building’s structural status from the respective stakeholders. Existing research has identified the benefits that Digital Twins can offer to achieve this aim. Therefore, this study aims to leverage and integrate a Digital Twin’s attributes of Machine Learning and Building Information Modelling (BIM), as well as visualise the results into a WEB dashboard to generate a rigorous, accurate, holistic, and user-friendly simulation method that can be implemented across all the phases of the disaster management lifecycle of a seismic excitation to improve building management processes.
To illustrate the results of the developed simulation method, a six-storey steel building is developed and used as a case study. The simulation method is developed in four phases: 1) Structural Analysis for Dataset Formulation, 2) Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) Model Generation, 3) BIM and ANN Model Integration and 4) Analysis and Visualisation of Insights.
Presentation
Conference Paper
Keywords
Digital Twin, Building Information Modelling, Artificial Neural Networks, WEB Dashboard, Disaster Operations Management.
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.47330/DCIO.2021.CUUX3225
Bibliography
PENDING